Oral version: CerebroPep
See our blog post & review:
Which Brain Peptide is Right for You? Our Selection roadmap 🗺️
It includes each product that contains CerebroPep & where to purchase

Benefits of Cerebrolysin / CerebroPep
Boosting cognitive function – memory, concentration, and thinking skills, improving mood, and enhancing the management of neurological conditions such as autism, ADHD, and cerebral palsy.
It also aids in nerve repair, treats hyperthermia-induced neurotoxicity and morphine withdrawal symptoms, improves eye health and much more.
It is used in the treatment of memory disorders, concentration disorders, and degenerative dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Numbers refer to studies referenced below
- Boosts cognitive function & brain performance for all ages [1-29]
- Improves mood [30-33]
- Improves symptoms of autism [34-36]
- Improves symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [37-38]
- Improves symptoms of cerebral palsy (CP) [39-42]
- Repairs nerve damage [43-49]
- Treats hyperthermia-induced neurotoxicity [50-51]
- Treats withdrawal symptoms [52-54]
- Boosts immune function [55-62]
- Improves eye health [63-64]
Key Takeaways
- Enhanced Cognitive Abilities: Cerebrolysin is known for its ability to boost cognitive function, making it a potential treatment option for enhancing memory, concentration, and overall brain performance.
- Neurological Disorder Management: It shows promise in improving symptoms associated with various neurological disorders, including autism, ADHD, and cerebral palsy, providing a multifaceted approach to neurorehabilitation.
- Neuroprotection and Repair: Cerebrolysin has properties that facilitate nerve repair and protect against further neurological damage, which is particularly beneficial in conditions like stroke or traumatic brain injuries.
- Overall Health Improvement: Beyond neurological benefits, Cerebrolysin boosts immune function and improves eye health, demonstrating its versatility and broad therapeutic potential.
How They Work
The brain-boosting effects of cerebrolysin & Cerebropep are be attributed to the neuropeptides they contain.
These neuropeptides are active brain peptides (chains of amino acids) that are used by nerve cells (neurons) to enhance their communication with each other.
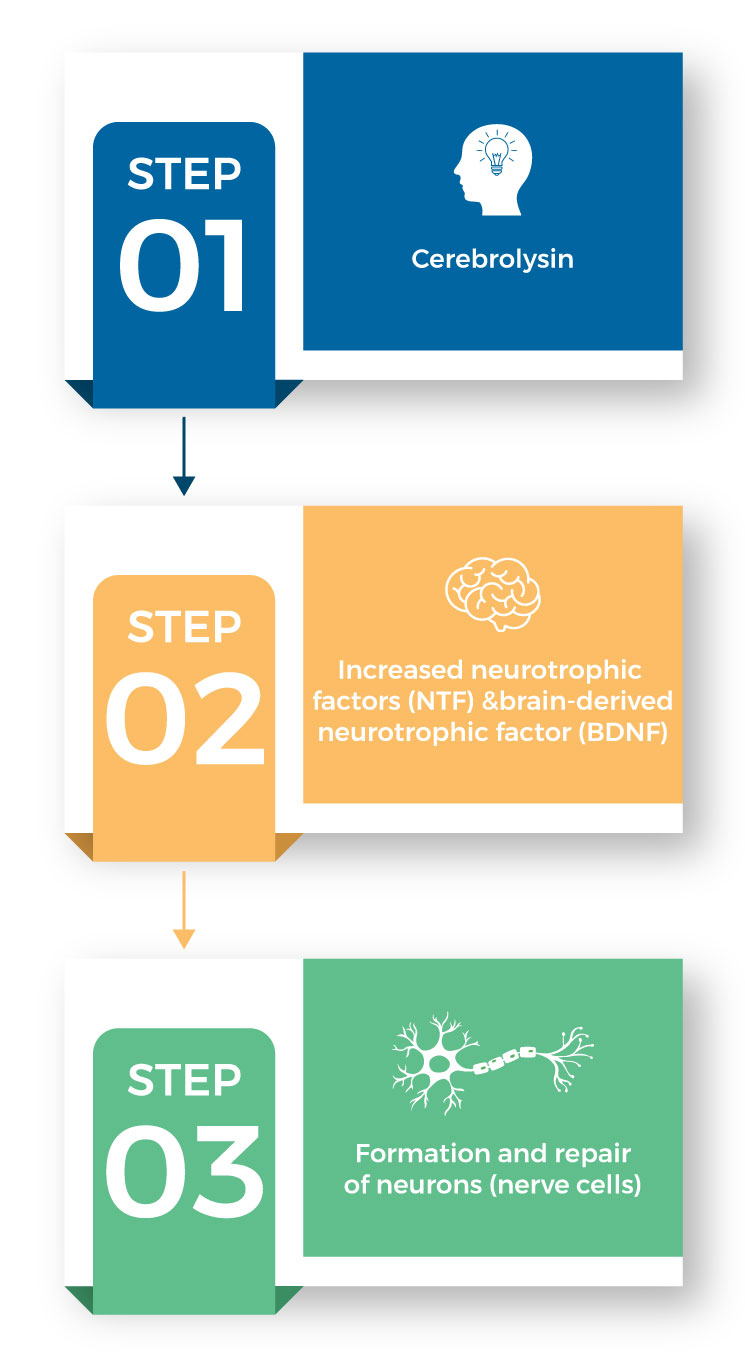
They work by increasing the levels of neurotrophic factors (NFT) and brain-derived neurotrophic factors.
This in turn stimulates the formation and repair of neurons (nerve cells) in the brain.
For Autism / ADHD Specifically
CogniPep contains oral Cerebrolysin (CerebroPep)
Our blog post is here: CogniPep is life changing for kids with Autism & ADHD

Studies listed by Genemedics
Research on Cerebrolysin
64 Related References
- Xiao S, Xue H, Li G. Therapeutic effects of cerebrolysin added to risperidone in patients with schizophrenia dominated by negative symptoms. The Australian and New Zealand journal of psychiatry. 2012; 46(2):153-60. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22311531View Summary +
- Crook TH, Ferris SH, Alvarez XA, Laredo M, Moessler H. Effects of N-PEP-12 on memory among older adults. International clinical psychopharmacology. 2005; 20(2):97-100. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15729085View Summary –Effects of N-PEP-12 on memory among older adultsThe study by Crook, Ferris, Alvarez, Laredo, and Moessler, published in International Clinical Psychopharmacology in 2005, examined the effects of N-PEP-12, a neuropeptide supplement, on memory among older adults. The double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involved 54 participants aged 50 or older who reported memory problems. The results suggested that N-PEP-12 may have a beneficial effect on memory performance in older adults with subjective memory complaints.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15729085
- Alvarez XA, Lombardi VR, Corzo L. Oral Cerebrolysin enhances brain alpha activity and improves cognitive performance in elderly control subjects. Journal of neural transmission. Supplementum. 2000; 59:315-28. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10961443View Summary –Oral Cerebrolysin enhances brain alpha activity and improves cognitive performance in elderly control subjectsThe study by Alvarez, Lombardi, and Corzo, published in the Journal of Neural Transmission Supplementum in 2000, investigated the effects of oral Cerebrolysin on brain alpha activity and cognitive performance in elderly subjects. This research observed an enhancement in brain alpha activity and an improvement in cognitive performance among elderly control subjects who were administered oral Cerebrolysin. The study contributes to understanding the potential cognitive benefits of Cerebrolysin in the elderly population.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10961443
- Allegri RF, Guekht A. Cerebrolysin improves symptoms and delays progression in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Drugs of today (Barcelona, Spain: 1998). 2012; 48 Suppl A:25-41. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22514793View Summary –Cerebrolysin improves symptoms and delays progression in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.The study by Allegri and Guekht, published in 2012 in “Drugs of Today”, examined the effects of Cerebrolysin on patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. The research suggested that Cerebrolysin not only improves symptoms but also delays the progression of these conditions. This study highlights the potential therapeutic benefits of Cerebrolysin in treating neurodegenerative diseases.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22514793
- Rockenstein E, Torrance M, Mante M. Cerebrolysin decreases amyloid-beta production by regulating amyloid protein precursor maturation in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of neuroscience research. 2006; 83(7):1252-61. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16511867View Summary –Cerebrolysin decreases amyloid-beta production by regulating amyloid protein precursor maturation in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s diseaseThe study by Rockenstein, Torrance, and Mante, published in the Journal of Neuroscience Research in 2006, investigated the impact of Cerebrolysin on amyloid-beta production in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. The research focused on the regulation of amyloid protein precursor maturation, finding that Cerebrolysin can reduce amyloid-beta production. This study contributes to the understanding of potential treatments for Alzheimer’s disease by targeting amyloid-beta pathways.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16511867
- Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Mante M. Effects of Cerebrolysin on amyloid-beta deposition in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of neural transmission. Supplementum. 2002. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12456076.View Summary –Effects of Cerebrolysin on amyloid-beta deposition in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s diseaseThe study by Rockenstein, Mallory, and Mante, published in 2002 in the Journal of Neural Transmission Supplementum, examined the effects of Cerebrolysin on amyloid-beta deposition in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. This research contributes to the understanding of how Cerebrolysin might influence the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, particularly in relation to amyloid-beta accumulation.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12456076
- Rockenstein E, Adame A, Mante M, Moessler H, Windisch M, Masliah E. The neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease are associated with improved behavioral performance. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996). 2003; 110(11):1313-27. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14628195View Summary –The neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease are associated with improved behavioral performance.The study by Rockenstein, Adame, Mante, Moessler, Windisch, and Masliah, published in the Journal of Neural Transmission in 2003, focused on the neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. The research demonstrated that Cerebrolysin is associated with improved behavioral performance, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent in Alzheimer’s disease management. For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14628195
- Ladurner G, Kalvach P, Moessler H, .Neuroprotective treatment with cerebrolysin in patients with acute stroke: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996). 2005; 112(3):415-28. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15583955View Summary –Neuroprotective treatment with cerebrolysin in patients with acute stroke: a randomised controlled trialThe study by Ladurner, Kalvach, and Moessler, published in the Journal of Neural Transmission in 2005, investigated the neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin in patients with acute stroke in a randomised controlled trial. The research aimed to evaluate the potential benefits of Cerebrolysin in acute stroke management.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15583955
- Muresanu DF, Heiss W-D, Hoemberg V, et al. Cerebrolysin and Recovery After Stroke (CARS): A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Multicenter Trial. Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation. 2016;47(1):151-159. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009416. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4689177/.View Summary –Cerebrolysin and Recovery After Stroke (CARS): A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Multicenter TrialThe study by Muresanu, Heiss, Hoemberg, and colleagues, published in 2016 in the journal “Stroke,” was a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial titled “Cerebrolysin and Recovery After Stroke (CARS).” It focused on evaluating the efficacy of Cerebrolysin in stroke recovery. The trial aimed to determine how Cerebrolysin affects the recovery process after a stroke.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4689177/
- Guekht A, Vester J, Heiss WD. Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in motor function recovery after stroke: a meta-analysis of the CARS trials. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2017; 38(10):1761-1769. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28707130.View Summary –Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in motor function recovery after stroke: a meta-analysis of the CARS trialsThe 2017 study by Guekht, Vester, and Heiss, published in Neurological Sciences, is a meta-analysis of the CARS trials focusing on the safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in motor function recovery after stroke. This comprehensive analysis consolidates findings from various studies to evaluate the overall impact of Cerebrolysin on stroke recovery, particularly in terms of motor function.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28707130
- Chen CC, Wei ST, Tsaia SC, Chen XX, Cho DY. Cerebrolysin enhances cognitive recovery of mild traumatic brain injury patients: double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study. British journal of neurosurgery. 2013; 27(6):803-7. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23656173.View Summary –Cerebrolysin enhances cognitive recovery of mild traumatic brain injury patients: double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized studyThe study by Chen, Wei, Tsaia, Chen, and Cho, published in the British Journal of Neurosurgery in 2013, was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study that investigated the effects of Cerebrolysin on cognitive recovery in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. The study demonstrated that Cerebrolysin enhances cognitive recovery in these patients.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23656173
- Bornstein N, Poon WS. Accelerated recovery from acute brain injuries: clinical efficacy of neurotrophic treatment in stroke and traumatic brain injuries. Drugs of today (Barcelona, Spain : 1998). 2012; 48 Suppl A:43-61. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22514794View Summary –Accelerated recovery from acute brain injuries: clinical efficacy of neurotrophic treatment in stroke and traumatic brain injuriesThe study by Bornstein and Poon, published in 2012 in “Drugs of Today,” discusses the clinical efficacy of neurotrophic treatment in accelerating recovery from acute brain injuries, particularly focusing on stroke and traumatic brain injuries. The research provides insights into the potential benefits of such treatments in enhancing recovery processes.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22514794
- Wong GK, Zhu XL, Poon WS. Beneficial effect of cerebrolysin on moderate and severe head injury patients: result of a cohort study. Actaneurochirurgica. Supplement. 2005; 95:59-60. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16463821.View Summary –Beneficial effect of cerebrolysin on moderate and severe head injury patients: result of a cohort studyThe study by Wong, Zhu, and Poon, published in “Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement” in 2005, explored the beneficial effects of cerebrolysin on patients with moderate and severe head injuries. This cohort study contributes to the understanding of cerebrolysin’s role in treating head injury cases.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16463821
- Zhang D, Dong Y, Li Y, Chen J, Wang J, Hou L. Efficacy and Safety of Cerebrolysin for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BioMed Research International. 2017;2017:4191670. doi:10.1155/2017/4191670. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5474547/.View Summary –Efficacy and Safety of Cerebrolysin for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled TrialsThe 2017 study by Zhang, Dong, Li, Chen, Wang, and Hou, published in BioMed Research International, is a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials assessing the efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin for treating acute ischemic stroke. This comprehensive analysis aims to provide insights into the therapeutic benefits and safety profile of Cerebrolysin in this context.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5474547/
- Hassanein SM, Deifalla SM, El-Houssinie M, Mokbel SA. Safety and Efficacy of Cerebrolysin in Infants with Communication Defects due to Severe Perinatal Brain Insult: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of clinical neurology (Seoul, Korea). 2016; 12(1):79-84. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26365023.Ozkizilcik A, Sharma A, Muresanu DF. Timed Release of Cerebrolysin Using Drug-Loaded TitanateNanospheres Reduces Brain Pathology and Improves Behavioral Functions in Parkinson’s Disease. Molecular neurobiology. 2017. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28875428.View Summary –Safety and Efficacy of Cerebrolysin in Infants with Communication Defects due to Severe Perinatal Brain Insult: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialThe study by Hassanein, Deifalla, El-Houssinie, and Mokbel, published in the Journal of Clinical Neurology in 2016, was a randomized controlled clinical trial investigating the safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in infants with communication defects due to severe perinatal brain insult. The study contributes to the understanding of potential treatments for infants affected by these conditions.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26365023
- Ozkizilcik A, Sharma A, Muresanu DF. Timed Release of Cerebrolysin Using Drug-Loaded TitanateNanospheres Reduces Brain Pathology and Improves Behavioral Functions in Parkinson’s Disease. Molecular neurobiology. 2017. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28875428.View Summary –Timed Release of Cerebrolysin Using Drug-Loaded TitanateNanospheres Reduces Brain Pathology and Improves Behavioral Functions in Parkinson’s DiseaseThe 2017 study by Ozkizilcik, Sharma, and Muresanu, published in Molecular Neurobiology, focused on the use of drug-loaded titanate nanospheres for the timed release of Cerebrolysin in Parkinson’s disease. This innovative approach aimed to reduce brain pathology and improve behavioral functions in Parkinson’s disease, marking a significant advancement in the treatment strategies for this condition.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28875428
- Requejo C, Ruiz-Ortega JA, Cepeda H. Nanodelivery of Cerebrolysin and Rearing in Enriched Environment Induce Neuroprotective Effects in a Preclinical Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecular neurobiology. 2017. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28840482.View Summary –Nanodelivery of Cerebrolysin and Rearing in Enriched Environment Induce Neuroprotective Effects in a Preclinical Rat Model of Parkinson’s DiseaseThe 2017 study by Requejo, Ruiz-Ortega, and Cepeda, published in Molecular Neurobiology, explores the neuroprotective effects of nanodelivery of Cerebrolysin combined with rearing in an enriched environment in a preclinical rat model of Parkinson’s disease. This innovative approach aimed to study the combined effects of advanced drug delivery and environmental factors on Parkinson’s disease pathology. For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28840482
- Noor NA, Mohammed HS, Mourad IM, Khadrawy YA, AboulEzz HS. A promising therapeutic potential of cerebrolysin in 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Life sciences. 2016; 155:174-9. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27210889View Summary –A promising therapeutic potential of cerebrolysin in 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease.The 2016 study by Noor, Mohammed, Mourad, Khadrawy, and AboulEzz, published in Life Sciences, investigated the therapeutic potential of cerebrolysin in a 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease. The study focused on assessing the effectiveness of cerebrolysin in treating Parkinson’s disease symptoms and its potential as a therapeutic option.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27210889
- KalynIaB, Safarova TP, Sheshenin VC, Gavrilova SI. [Comparative efficacy and safety of antidepressant mono- and multimodal therapy in elderly patients with depression (a clinical experience in a psychogeriatric hospital)]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. 2014; 114(6 Pt 2):20-9. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25042499.View Summary –Comparative efficacy and safety of antidepressant mono- and multimodal therapy in elderly patients with depression (a clinical experience in a psychogeriatric hospital)The 2014 study by Kalyn, Safarova, Sheshenin, and Gavrilova, published in the Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, focused on comparing the efficacy and safety of antidepressant mono- and multimodal therapy in elderly patients with depression, based on clinical experiences in a psychogeriatric hospital. This research provides valuable insights into the treatment strategies for depression in the elderly. For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25042499
- Gharagozli, K., Harandi, A. A., Houshmand, S., Akbari, N., Muresanu, D. F., Vester, J., Winter, S., & Moessler, H. (2017). Efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin treatment in early recovery after acute ischemic stroke: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter clinical trial. Journal of medicine and life, 10(3), 153–160.View Summary –Efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin treatment in early recovery after acute ischemic stroke: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter clinical trialThe study by Gharagozli, Harandi, Houshmand, Akbari, Muresanu, Vester, Winter, and Moessler, published in the Journal of Medicine and Life in 2017, is a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter clinical trial that examined the efficacy and safety of Cerebrolysin treatment in the early recovery phase after acute ischemic stroke. This research contributes to the understanding of Cerebrolysin’s role in stroke recovery.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5652261/
- Masliah, E., & Díez-Tejedor, E. (2012). The pharmacology of neurotrophic treatment with Cerebrolysin: brain protection and repair to counteract pathologies of acute and chronic neurological disorders. Drugs of today (Barcelona, Spain : 1998), 48 Suppl A, 3–24. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2012.48(Suppl.A).1739716View Summary – The pharmacology of neurotrophic treatment with Cerebrolysin: brain protection and repair to counteract pathologies of acute and chronic neurological disordersThe 2012 study by Masliah and Díez-Tejedor, published in “Drugs of Today,” explores the pharmacology of neurotrophic treatment with Cerebrolysin, emphasizing its potential in providing brain protection and aiding in repair processes. This study addresses the effectiveness of Cerebrolysin in combating both acute and chronic neurological disorders, offering insights into its therapeutic role and mechanism of action.For more details https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2012.48(Suppl.A).1739716
- Fiani, B., Covarrubias, C., Wong, A., Doan, T., Reardon, T., Nikolaidis, D., & Sarno, E. (2021). Cerebrolysin for stroke, neurodegeneration, and traumatic brain injury: review of the literature and outcomes. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology, 42(4), 1345–1353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05089-2View Summary –Cerebrolysin for stroke, neurodegeneration, and traumatic brain injury: review of the literature and outcomes.The 2021 study by Fiani, Covarrubias, Wong, Doan, Reardon, Nikolaidis, and Sarno, published in Neurological Sciences, provides a comprehensive review of Cerebrolysin’s use in treating stroke, neurodegeneration, and traumatic brain injury. This literature review and analysis of outcomes contribute to the understanding of Cerebrolysin’s therapeutic potential in these neurological conditions.For more details https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05089-2
- Zhang, C., Chopp, M., Cui, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, R., Zhang, L., Lu, M., Szalad, A., Doppler, E., Hitzl, M., & Zhang, Z. G. (2010). Cerebrolysin enhances neurogenesis in the ischemic brain and improves functional outcome after stroke. Journal of neuroscience research, 88(15), 3275–3281. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22495.View Summary –Cerebrolysin enhances neurogenesis in the ischemic brain and improves functional outcome after strokeThe 2010 study by Zhang, Chopp, Cui, Wang, Zhang, Lu, Szalad, Doppler, Hitzl, and Zhang, published in the Journal of Neuroscience Research, examines the role of Cerebrolysin in enhancing neurogenesis in the ischemic brain and its impact on functional outcomes after stroke. The study contributes to understanding the therapeutic potential of Cerebrolysin in stroke recovery and rehabilitation.For more details https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22495
- Bornstein, N. M., Guekht, A., Vester, J., Heiss, W. D., Gusev, E., Hömberg, V., Rahlfs, V. W., Bajenaru, O., Popescu, B. O., & Muresanu, D. (2018). Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in early post-stroke recovery: a meta-analysis of nine randomized clinical trials. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology, 39(4), 629–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-3214-0.View Summary –Safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in early post-stroke recovery: a meta-analysis of nine randomized clinical trials.The 2018 study by Bornstein, Guekht, Vester, Heiss, Gusev, Hömberg, Rahlfs, Bajenaru, Popescu, and Muresanu, published in Neurological Sciences, is a meta-analysis of nine randomized clinical trials assessing the safety and efficacy of Cerebrolysin in early post-stroke recovery. This comprehensive analysis synthesizes data from various studies to evaluate the overall impact of Cerebrolysin on stroke recovery.For more details https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-3214-0
- Heiss, W. D., Brainin, M., Bornstein, N. M., Tuomilehto, J., Hong, Z., & Cerebrolysin Acute Stroke Treatment in Asia (CASTA) Investigators (2012). Cerebrolysin in patients with acute ischemic stroke in Asia: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. Stroke, 43(3), 630–636. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.628537.View Summary –Cerebrolysin in patients with acute ischemic stroke in Asia: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial.The 2012 study by Heiss, Brainin, Bornstein, Tuomilehto, Hong, and the Cerebrolysin Acute Stroke Treatment in Asia (CASTA) Investigators, published in “Stroke,” was a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. It focused on the effects of Cerebrolysin in patients with acute ischemic stroke in Asia. The study contributes to the understanding of Cerebrolysin’s role in stroke treatment in this specific demographic.For more details https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.628537
- Chang, W. H., Lee, J., Shin, Y. I., Ko, M. H., Kim, D. Y., Sohn, M. K., Kim, J., & Kim, Y. H. (2021). Cerebrolysin Combined with Rehabilitation Enhances Motor Recovery and Prevents Neural Network Degeneration in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Severe Motor Deficits. Journal of personalized medicine, 11(6), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060545View Summary –Cerebrolysin Combined with Rehabilitation Enhances Motor Recovery and Prevents Neural Network Degeneration in Ischemic Stroke Patients with Severe Motor Deficits.The 2021 study by Chang, Lee, Shin, Ko, Kim, Sohn, Kim, and Kim, published in the Journal of Personalized Medicine, investigated the impact of combining Cerebrolysin with rehabilitation on motor recovery and prevention of neural network degeneration in ischemic stroke patients with severe motor deficits. This study provides insights into the potential benefits of integrating pharmacological and rehabilitation therapies for stroke recovery.For more details https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060545
- Tran, L., Alvarez, X. A., Le, H. A., Nguyen, D. A., Le, T., Nguyen, N., Nguyen, T., Nguyen, T., Vo, T., Tran, T., Duong, C., Nguyen, H., Nguyen, S., Nguyen, H., Le, T., Nguyen, M., & Nguyen, T. (2022). Clinical Efficacy of Cerebrolysin and Cerebrolysin plus Nootropics in the Treatment of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke in Vietnam. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets, 21(7), 621–630. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527320666210820091655View Summary –Clinical Efficacy of Cerebrolysin and Cerebrolysin plus Nootropics in the Treatment of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke in VietnamThe 2022 study by Tran, Alvarez, Le, and colleagues, published in CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets, evaluated the clinical efficacy of Cerebrolysin alone and in combination with nootropics for treating patients with acute ischemic stroke in Vietnam. The study provides important insights into treatment strategies for ischemic stroke, particularly in the context of these specific medical interventions.For more details https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527320666210820091655
- Stan, A., Birle, C., Blesneag, A., & Iancu, M. (2017). Cerebrolysin and early neurorehabilitation in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study. Journal of medicine and life, 10(4), 216–222.View Summary –Cerebrolysin and early neurorehabilitation in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study.The 2017 study by Stan, Birle, Blesneag, and Iancu, published in the Journal of Medicine and Life, was a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study assessing the effects of Cerebrolysin combined with early neurorehabilitation in patients with acute ischemic stroke. This research contributes to the understanding of the potential benefits of integrating pharmacological treatments with rehabilitation strategies in the early stages of stroke recovery.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5771251/
- Chen, N., Yang, M., Guo, J., Zhou, M., Zhu, C., & He, L. (2013). Cerebrolysin for vascular dementia. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, (1), CD008900. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008900.pub2 Summary –Cerebrolysin for vascular dementiaThe 2013 study by Chen, Yang, Guo, Zhou, Zhu, and He, published in The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, conducted a review on the use of Cerebrolysin for treating vascular dementia. This comprehensive analysis aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of Cerebrolysin in this context, contributing to the broader understanding of treatment options for vascular dementia.For more details see: here.
- Lang, W., Stadler, C. H., Poljakovic, Z., Fleet, D., & Lyse Study Group (2013). A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial about safety and efficacy of combined treatment with alteplase (rt-PA) and Cerebrolysin in acute ischaemic hemispheric stroke. International journal of stroke : official journal of the International Stroke Society, 8(2), 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2012.00901.x.View Summary –A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial about safety and efficacy of combined treatment with alteplase (rt-PA) and Cerebrolysin in acute ischaemic hemispheric stroke.The 2013 study by Lang, Stadler, Poljakovic, Fleet, and the Lyse Study Group, published in the International Journal of Stroke, was a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. It evaluated the safety and efficacy of a combined treatment with alteplase (rt-PA) and Cerebrolysin in acute ischemic hemispheric stroke. This research provides insights into the potential benefits of this combination therapy in stroke treatment.For more details https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2012.00901.x
- Panisset M, Gauthier S, Moessler H, Windisch M, .Cerebrolysin in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with a neurotrophic agent. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996). 2002; 109(7-8):1089-104. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12111446.View Summary –Cerebrolysin in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with a neurotrophic agentThe 2002 study by Panisset, Gauthier, Moessler, and Windisch, published in the Journal of Neural Transmission, was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigating the efficacy of Cerebrolysin in Alzheimer’s disease. This trial aimed to assess the potential benefits of Cerebrolysin, a neurotrophic agent, in treating Alzheimer’s disease.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12111446
- Retrieved from View Summary
- Shabanov PD, Lebedev AA, Pavlenko VP, Ganapol’skiĭ VP. [Comparative study of behavioral effects of cortexin and cerebrolysine upon intraventricular and intraperitoneal administration in rats]. Eksperimental’naia i klinicheskaiafarmakologiia. ; 70(3):13-9. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17650626 –Comparative study of behavioral effects of cortexin and cerebrolysine upon intraventricular and intraperitoneal administration in rats The study by Shabanov, Lebedev, Pavlenko, and Ganapol’skiĭ, published in Eksperimental’naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia, compares the behavioral effects of cortexin and cerebrolysin administered intraventricularly and intraperitoneally in rats. This research contributes to the understanding of the behavioral impacts of these substances in animal models.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17650626
- Krasnoperova MG, Bashina VM, Skvortsov IA, Simashkova NV. [The effect of Cerebrolysin on cognitive functions in childhood autism and in Asperger syndrome]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. 2003; 103(6):15-8. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12872620. –The effect of cerebrolysin on cognitive functions in childhood autism and in Asperger syndrome — The study by Krasnoperova, Bashina, Skvortsov, and Simashkova, published in 2003 in the Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, investigated the effect of cerebrolysin on cognitive functions in children with autism and Asperger syndrome. The study aimed to assess the potential benefits of cerebrolysin in improving cognitive functions in these conditions. For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12872620
- Chutko LS, Yakovenko EA, Surushkina SY, Kryukova EM, Palaieva SV. [The efficacy of cerebrolysin in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. 2017; 117(9):71-75. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29053124. The efficacy of cerebrolysin in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders — The 2017 study by Chutko, Yakovenko, Surushkina, Kryukova, and Palaieva, published in the Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, explored the efficacy of cerebrolysin in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders. This study contributes to the growing body of research on potential treatments for autism spectrum disorders. For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29053124
- Cuevas-Olguin R, Roychowdhury S, Banerjee A. Cerebrolysin prevents deficits in social behavior, repetitive conduct, and synaptic inhibition in a rat model of autism. Journal of neuroscience research. 2017; 95(12):2456-2468. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28609577 Cerebrolysin prevents deficits in social behavior, repetitive conduct, and synaptic inhibition in a rat model of autism — The 2017 study by Cuevas-Olguin, Roychowdhury, and Banerjee, published in the Journal of Neuroscience Research, examined the effects of Cerebrolysin in a rat model of autism. The study focused on how Cerebrolysin impacts social behavior, repetitive conduct, and synaptic inhibition, offering insights into potential therapeutic approaches for autism. For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28609577
- Sotnikova NY, Gromova OA, Novicova EA. Dual effect of cerebrolysin in children with attention deficit syndrome with hyperactivity: neuroprotection and immunomodulation. Russian journal of immunology : RJI : official journal of Russian Society of Immunology. 2002; 7(4):357-64. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12687248 –Dual effect of cerebrolysin in children with attention deficit syndrome with hyperactivity: neuroprotection and immunomodulation — The 2002 study by Sotnikova, Gromova, and Novicova, published in the Russian Journal of Immunology, investigated the dual effect of Cerebrolysin in children with attention deficit syndrome with hyperactivity. The study focused on both the neuroprotective and immunomodulatory effects of Cerebrolysin, providing insights into its potential therapeutic applications.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12687248
- Chutko LS, Yakovenko EA, Surushkina SY, Anisimova TI, Kropotov YD. [Clinical and neurophysiological heterogeneity of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. ; 116(10):117-121. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27845323 –Clinical and neurophysiological heterogeneity of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder — The 2016 study by Chutko, Yakovenko, Surushkina, Anisimova, and Kropotov, published in the Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, discusses the clinical and neurophysiological heterogeneity of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This study contributes to the understanding of ADHD’s diverse clinical presentations and underlying neurophysiological mechanisms.For more details https://europepmc.org/article/med/27845323
- Nasiri J, Safavifar F. Effect of cerebrolysin on gross motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a clinical trial. ActaneurologicaBelgica. 2017; 117(2):501-505. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28074392 –Effect of cerebrolysin on gross motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a clinical trial — The 2017 clinical trial by Nasiri and Safavifar, published in Acta Neurologica Belgica, evaluated the effect of cerebrolysin on the gross motor function of children with cerebral palsy. This study contributes to the understanding of potential therapeutic interventions for improving motor function in children with this condition.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28074392
- Gershman RN, Vasilenko MA. [Use of cerebrolysin and ATP in treating infantile cerebral paralysis]. Pediatriiaakusherstvo i ginekologiia.. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1228606
- Retrieved from here
- Retrieved from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02116348
- Biesenbach G, Grafinger P, Eichbauer-Sturm G, Zazgornik J. [Cerebrolysin in treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy]. Wiener medizinischeWochenschrift (1946). 1997; 147(3):63-6. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9173675.View Summary –Cerebrolysin in treatment of painful diabetic neuropathyThe 1997 study by Biesenbach, Grafinger, Eichbauer-Sturm, and Zazgornik, published in Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift, investigated the use of Cerebrolysin in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. This study contributes to the understanding of potential treatment options for managing neuropathic pain in individuals with diabetes.For more details https://europepmc.org/article/med/9173675
- Dong H, Jiang X, Niu C, Du L, Feng J, Jia F. Cerebrolysin improves sciatic nerve dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Neural Regeneration Research. 2016;11(1):156-162. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.175063. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4774211/View Summary -The study by Dong, Jiang, Niu, Du, Feng, and Jia, published in Neural Regeneration Research in 2016, investigated the effects of Cerebrolysin on sciatic nerve dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This research explored the potential benefits of Cerebrolysin in improving nerve function in the context of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4774211/
- Retrieved from here
- Masliah E, Armasolo F, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Samuel W. Cerebrolysin ameliorates performance deficits, and neuronal damage in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior. 1999; 62(2):239-45. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9972690.View Summary –Cerebrolysin ameliorates performance deficits, and neuronal damage in apolipoprotein E-deficient miceThe 1999 study by Masliah, Armasolo, Veinbergs, Mallory, and Samuel, published in Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, investigated the effects of Cerebrolysin in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. The study aimed to assess the impact of Cerebrolysin on performance deficits and neuronal damage in this mouse model.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9972690
- Keilhoff G, Lucas B, Pinkernelle J, Steiner M, Fansa H. Effects of cerebrolysin on motor-neuron-like NSC-34 cells. Experimental cell research. 2014; 327(2):234-55. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24997385.View Summary –Effects of cerebrolysin on motor-neuron-like NSC-34 cellsThe 2014 study by Keilhoff, Lucas, Pinkernelle, Steiner, and Fansa, published in Experimental Cell Research, examined the effects of Cerebrolysin on motor-neuron-like NSC-34 cells. The research aimed to investigate the impact of Cerebrolysin on these cells, providing insights into its potential effects on motor neuron function.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24997385
- Shchudlo NA, Shchudlo MM, Borisova IV. [The effect of cerebrolysin on the regeneration of the peripheral nerve depending on the scheme of paraneural administration]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. 2013; 113(12):76-80. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24430040.View Summary –The effect of cerebrolysin on the regeneration of the peripheral nerve depending on the scheme of paraneural administrationThe 2013 study by Shchudlo, Shchudlo, and Borisova, published in Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, examined the effect of Cerebrolysin on the regeneration of peripheral nerves, depending on the scheme of paraneural administration. This research contributes to our understanding of how the administration of Cerebrolysin may impact peripheral nerve regeneration.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24430040
- Available from here
- Sharma HS, Sharma A, Mössler H, Muresanu DF. Neuroprotective effects of cerebrolysin, a combination of different active fragments of neurotrophic factors and peptides on the whole body hyperthermia-induced neurotoxicity: modulatory roles of co-morbidity factors and nanoparticle intoxication. International review of neurobiology. 2012; 102:249-76. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22748833.View Summary –Neuroprotective effects of cerebrolysin, a combination of different active fragments of neurotrophic factors and peptides on the whole body hyperthermia-induced neurotoxicity: modulatory roles of co-morbidity factors and nanoparticle intoxicationThe 2012 study by Sharma, Sharma, Mössler, and Muresanu, published in the International Review of Neurobiology, investigated the neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin on whole-body hyperthermia-induced neurotoxicity. The study explored the potential benefits of Cerebrolysin and its modulation by co-morbidity factors and nanoparticle intoxication.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22748833
- Sharma A, Muresanu DF, Mössler H, Sharma HS. Superior neuroprotective effects of cerebrolysin in nanoparticle-induced exacerbation of hyperthermia-induced brain pathology. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets. 2012; 11(1):7-25. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22229316.View Summary –Superior neuroprotective effects of cerebrolysin in nanoparticle-induced exacerbation of hyperthermia-induced brain pathologyThe 2012 study by Sharma, Muresanu, Mössler, and Sharma, published in CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets, investigated the superior neuroprotective effects of Cerebrolysin in the context of nanoparticle-induced exacerbation of hyperthermia-induced brain pathology. The study explored how Cerebrolysin may provide enhanced protection in this scenario.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22229316
- Martínez-Laorden E, Hurle MA, Milanés MV, Laorden ML, Almela P. Morphine withdrawal activates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and heat shock protein 27 in the left ventricle: the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2012; 342(3):665-75. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22647273.View Summary –Morphine withdrawal activates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and heat shock protein 27 in the left ventricleThe 2012 study by Martínez-Laorden, Hurle, Milanés, Laorden, and Almela, published in The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, examined the effects of morphine withdrawal on the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) in the left ventricle of the heart. The study also explored the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in this processFor more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22647273
- Sharma HS, Ali SF, Patnaik R, Zimmermann-Meinzingen S, Sharma A, Muresanu DF. Cerebrolysin Attenuates Heat Shock Protein (HSP 72 KD) Expression in the Rat Spinal Cord Following Morphine Dependence and Withdrawal: Possible New Therapy for Pain Management. Current neuropharmacology. 2011; 9(1):223-35. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21886595.View Summary –Cerebrolysin Attenuates Heat Shock Protein (HSP 72 KD) Expression in the Rat Spinal Cord Following Morphine Dependence and Withdrawal: Possible New Therapy for Pain ManagementThe 2011 study by Sharma, Ali, Patnaik, Zimmermann-Meinzingen, Sharma, and Muresanu, published in Current Neuropharmacology, investigated the effects of Cerebrolysin on the expression of heat shock protein (HSP 72 KD) in the rat spinal cord following morphine dependence and withdrawal. The study explored the potential therapeutic use of Cerebrolysin for pain management.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21886595
- Belokrylov GA, Malchanova IV. [Levamin and cerebrolysin as immunostimulants]. Biulleten’ eksperimental’noibiologii i meditsiny. 1992; 113(2):165-6. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1611065.View Summary –Levamin and cerebrolysin as immunostimulantsThe 1992 study by Belokrylov and Malchanova, published in Biulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, explored the immunostimulant effects of Levamin and Cerebrolysin. The study investigated their potential as immunostimulants, which are substances that enhance the immune system’s activity.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1611065
- Govorin NV, Zlova TP, Akhmetova VV, Tarasova OA. [The pathophysiological analysis of cerebrolysin therapy of children with mental developmental delay caused by ecological factors]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. 2008; 108(5):51-5. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18577958.View Summary –The pathophysiological analysis of cerebrolysin therapy of children with mental developmental delay caused by ecological factorsThe 2008 study by Govorin, Zlova, Akhmetova, and Tarasova, published in Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, conducted a pathophysiological analysis of Cerebrolysin therapy in children with mental developmental delay caused by ecological factors. The study aimed to assess the effects of Cerebrolysin treatment in this specific group of children.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18577958
- Sotnikova NY, Gromova OA, Novikova EA, Burtsev EM. Immunoactive Properties of Cerebrolysin. Russian journal of immunology : RJI : official journal of Russian Society of Immunology. 2000; 5(1):63-70. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12687163.View Summary –Immunoactive Properties of CerebrolysinThe 2000 study by Sotnikova, Gromova, Novikova, and Burtsev, published in the Russian Journal of Immunology, focused on the immunoactive properties of Cerebrolysin. The study aimed to investigate how Cerebrolysin affects the immune system, particularly its immunoactive properties.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12687163
- Garmanchuk LV, Perepelitsyna EM, SidorenkoMv, Makarenko AN, Kul’chikov AE. [Cytoprotective effect of neuropeptides on immunocompetent cells (in vitro study)]. Eksperimental’naia i klinicheskaiafarmakologiia. ; 72(4):28-32. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19803367View Summary –Cytoprotective effect of neuropeptides on immunocompetent cells (in vitro study)The study conducted by Garmanchuk, Perepelitsyna, Sidorenko, Makarenko, and Kul’chikov, published in Eksperimental’naia i Klinicheskaia Farmakologiia, investigated the cytoprotective effect of neuropeptides on immunocompetent cells in an in vitro study. This research focused on how neuropeptides, which include substances like Cerebrolysin, impact the protection of immunocompetent cells.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19803367
- González ME, Francis L, Castellano O. Antioxidant systemic effect of short-term Cerebrolysin administration. Journal of neural transmission. Supplementum. 1998; 53:333-41. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9700669.View Summary –Antioxidant systemic effect of short-term Cerebrolysin administrationThe study conducted by González, Francis, and Castellano, published in the Journal of Neural Transmission – Supplementum in 1998, focused on the antioxidant systemic effect of short-term Cerebrolysin administration. The research aimed to investigate how short-term administration of Cerebrolysin affects the antioxidant system in the body.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9700669
- Gromova OA, Avdeenko TV, Burtsev EM, Skal’nyĭ AV, Solov’ev OI. [Effects of cerebrolysin on the oxidant homeostasis, the content of microelements and electrolytes in children with minimal brain dysfunction]. Zhurnalnevrologii i psikhiatriiimeni S.S. Korsakova. 1998; 98(1):27-30. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9505400.View Summary –Effects of cerebrolysin on the oxidant homeostasis, the content of microelements and electrolytes in children with minimal brain dysfunctionThe study conducted by Gromova, Avdeenko, Burtsev, Skal’nyĭ, and Solov’ev, published in Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova in 1998, investigated the effects of Cerebrolysin on the oxidant homeostasis, the content of microelements, and electrolytes in children with minimal brain dysfunction. The research aimed to assess how Cerebrolysin impacts these parameters in children with minimal brain dysfunction.For more details https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9505400
- Retrieved from View Summary –
- González ME, Francis L, Castellano O. Antioxidant systemic effect of short-term Cerebrolysin administration. Journal of neural transmission. Supplementum. 1998; 53:333-41. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9700669.View Summary –Antioxidant systemic effect of short-term Cerebrolysin administration. Journal of neural transmissionThe study titled “Antioxidant systemic effect of short-term Cerebrolysin administration” was published in the Journal of Neural Transmission – Supplementum in 1998. Unfortunately, I’m unable to access the specific content of the linked article directly. However, based on the title, it suggests that the study investigated the antioxidant effects of short-term Cerebrolysin administration.For more details https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-7091-6467-9_29
- Retrieved from http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/9505400.View Summary
- Huang TL, Huang SP, Chang CH, Lin KH, Sheu MM, Tsai RK. Protective effects of cerebrolysin in a rat model of optic nerve crush. The Kaohsiung journal of medical sciences. 2014; 30(7):331-6. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24924838.View Summary –Protective effects of cerebrolysin in a rat model of optic nerve crushThe study titled “Protective effects of cerebrolysin in a rat model of optic nerve crush” was published in The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences in 2014. This study investigated the potential protective effects of Cerebrolysin in a rat model of optic nerve crush, a condition that can lead to optic nerve damage and vision impairment.For more details https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1607551X1400062X
- Retrieved from http://www.roneurosurgery.eu/atdoc/16CostinDCombined.pdf
Other Peptides:
See: https://diaryofrecovery.com/resources
Recent Posts
- I’ll Show You Mine…. (peptide stack)

- Better healing through better sleep – yes you can!

- Which Brain Peptide is Right for You? New Spray reviewed & selection roadmap 🗺️

- Plavelle Peptide: Jack of many trades for proactive healing

- Allergy, Asthma, MCAS Freedom! These peptides beat our meds

- Make the switch! Peptide replacements for herbs, supps & more

- His & Hers Peptides — ways we support hormones Over 40

- 7 breakthrough Peptides for Autism, ADHD and more!

